12.4 months
—
longer than that reported in vemurafenib
(5.3 months; ref. 23) and dabrafenib (4.5
–
6.2 months) in the
same setting (24). Data from the randomized COLUMBUS
trial con
fi
rm this observation (25).
Encorafenib was well tolerated, with most AEs being grade 2
or lower in severity. Single-agent BRAFis have been associated
with characteristic AEs, which are proposed to be the result of
escalation and expansion phases. PPED and hyperkeratosis
were reported in over 40% of patients, higher than the rates
reported with the approved BRAF inhibitors. Although hyper-
keratosis is a characteristic and diagnostic feature of PPED
according to the NCI CTCAE v4.0 reporting criteria (18),
hyperkeratosis was often experienced in locations other
than the hands and feet. Cutaneous SCC has been reported in
100
80
Best % change
from baseline
-120
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
-100
60
40
20
V600E mutation
V600K mutation
Other mutation
Treatment group
Treatment group
100
80
Best % change
from baseline
-120
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
-100
60
40
20
100
80
-120
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
-100
60
40
20
BRAFi-pretreated
V600E mutation
V600K mutation
Other mutation
V600E mutation
Other mutation
(
n
= 30)
A
B
C
100
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Time (months)
Probability event-free, %
101112131415161718 20 19
151010 9 9 9 9 9 7 7 4 4 4 2 1 0 0 0 0 00
0
20
60
40
80
BRAFi-pretreated: 1.91 [0.92; 3.68]
D
Censoring times
BRAFi-pretreated
Number of patients still at risk
1811 8 5 3 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 01
BRAFi-pretreated
100
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Time (months)
Probability event-free, %
101112131415161718 20 21
0
0
19
15131313121212121010 6 6 5 2 1 1 0 0 0 00
0
20
60
40
80
Censoring times
BRAFi-pretreated
Number of patients still at risk
18171511 9 8 8 8 8 8 6 4 4 4 3 3 1 1 1 11
BRAFi-pretreated
Median progression-free survival, months
Median overall survival, months
BRAFi-pretreated: 9.07 [3.68; 10.84]
BRAF Status
BRAFi-naïve
(
n
= 28)
(
n
= 23)
BRAF Status
BRAFi-
naïve
: 12.35 [7.43; NA]
BRAFi-naïve
BRAFi-naïve
BRAFi-naïve
BRAFi-naïve
BRAFi-
naïve
: NA
BRAF Status
150 mg once daily
75 mg twice daily
100 mg once daily
50 mg once daily
300 mg once daily
200 mg once daily
150 mg twice daily
100 mg twice daily
550 mg once daily
450 mg once daily
700 mg once daily
BRAFi-pretreated 300 mg once daily
BRAFi-pretreated 450 mg once daily
BRAFi-naïve 450 mg once daily
BRAFi-naïve 300 mg once daily
Step-wise group
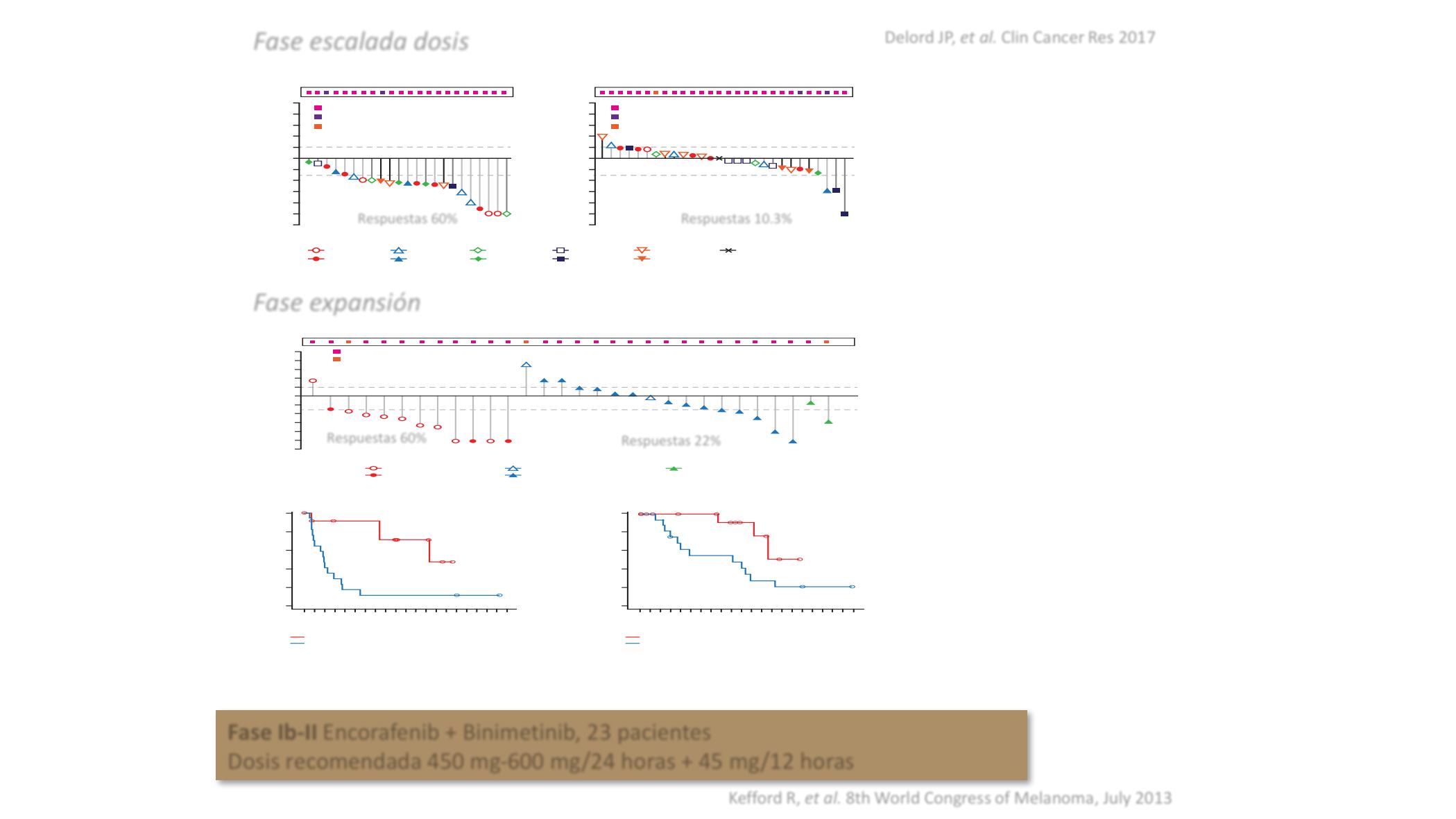
Figure 3.
Ef
fi
cacy of encorafenib by treatment
group. Best percentage of change in
sum of longest diameters in target
lesion from baseline by treatment
group in the dose-escalation (
A
) and
dose-expansion phases (
B
), Kaplan
–
Meier plot of progression-free survival
(
C
), and overall survival (
D
), by patient
group in the dose-escalation phase.
NA, not applicable.
Delord et al.
Delord JP,
et al.
Clin Cancer Res 2017
Fase escalada dosis
12.4 months
—
longer than that reported in vemurafenib
(5.3 months; ref. 23) and dabrafenib (4.5
–
6.2 months) in the
same setting (24). Data from the randomized COLUMBUS
trial con
fi
rm this observation (25).
Encorafenib was well tolerated, with most AEs being grade 2
or lower in severity. Si gle- gent BRAFis have bee associated
with characteristic AEs, which are proposed to be the result of
aberrant wild-type BRAF/CRAF activation. Dermatologic events
were among the most common AEs observed in the dose
escalation and expansion phases. PPED and hyperkeratosis
were reported in over 40% of patients, higher than the rates
reported with the approved BRAF inhibitors. Although hyper-
keratosis is a characteristic and diagnostic feature of PPED
according to the NCI CTCAE v4.0 reporting criteria (18),
hyperkeratosis was often ex erie ced in locations other
than he hands and feet. Cutaneous SCC has been reported in
12%
–
21% of patients w th melanoma following treatment
with vemurafenib monotherapy (23, 26, 27) and in 9%
–
100
Best % change
from baseline
-120
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
-100
6
40
20
V600E mutation
V600K mutation
Other mutation
Treatment group
Treatment group
100
80
Best % change
from baseline
-120
0
-20
-40
-6
-80
-100
60
2
100
-120
0
-2
-4
-60
-80
-100
6
40
20
BRAFi-pretreated
V600E mutation
V600K mutation
Other mutation
V600E mutation
Other mutation
(
n
= 30)
A
B
C
100
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Time (months)
Probability event-free, %
101112131415161718 20 19
151010 9 9 9 9 9 7 7 4 4 4 2 1 0 0 0 0 00
0
20
60
80
BRAFi-pretreated: 1.91 [0.92; 3.68]
D
Censoring times
BRAFi-pretreated
Number of patients still at risk
1811 8 5 3 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 01
BRAFi-pretreated
100
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Time (months)
Probability event-free, %
101112131415161718 20 21
0
0
19
15131313121212121010 6 6 5 2 1 1 0 0 0 00
0
20
60
0
80
Censoring times
BRAFi-pretreated
Number of patients still at risk
18171511 9 8 8 8 8 8 6 4 4 4 3 3 1 1 1 11
BRAFi-pretreated
Median progr ssion-free survival, months
Median ov r ll survival, months
BRAFi-pretreated: 9.07 [3.68; 10.84]
BRAF Status
BRAFi-naïve
(
n
= 28)
(
n
= 23)
BRAF Status
BRAFi-
naïve
: 12.35 [7.43; NA]
BRAFi-naïve
BRAFi-naïve
BRAFi-naïve
BRAFi-naïve
BRAFi-
naïve
: NA
BRAF Status
150 mg once daily
75 mg twice daily
100 mg once daily
50 mg once daily
300 mg once daily
200 mg once daily
150 mg twice daily
100 mg twice daily
550 mg once daily
450 mg once daily
700 mg once daily
BRAFi-pretreated 300 mg once daily
BRAFi-pretreated 450 mg once daily
BRAFi-naïve 450 mg once daily
BRAFi-naïve 300 mg once daily
Step-wise group
Figure 3.
Ef
fi
cacy of ncoraf nib by treatme t
group. Best percentage of change in
sum of longest diameters in target
lesion from baseline by treatment
group in the dose-escalation (
A
) and
d se-expansion phases (
B
), Kaplan
–
Meier plot of progression-free survival
(
C
), and overall survival (
D
), by patient
group in the dose-escalation phase.
NA, not applicable.
Delord et al.
Published OnlineFirst June 13, 2017; DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2923
Fase expansión
Respuestas 60%
Respuestas 10.3%
Respuestas 60%
Respuestas 22%
Fase Ib-II
Encor fenib + Binimetinib, 23 pacient s
Dosis recomendada 450 mg-600 mg/24 horas + 45 mg/12 horas
Kefford R,
et al.
8 h World ongress of Melanoma, July 2013








