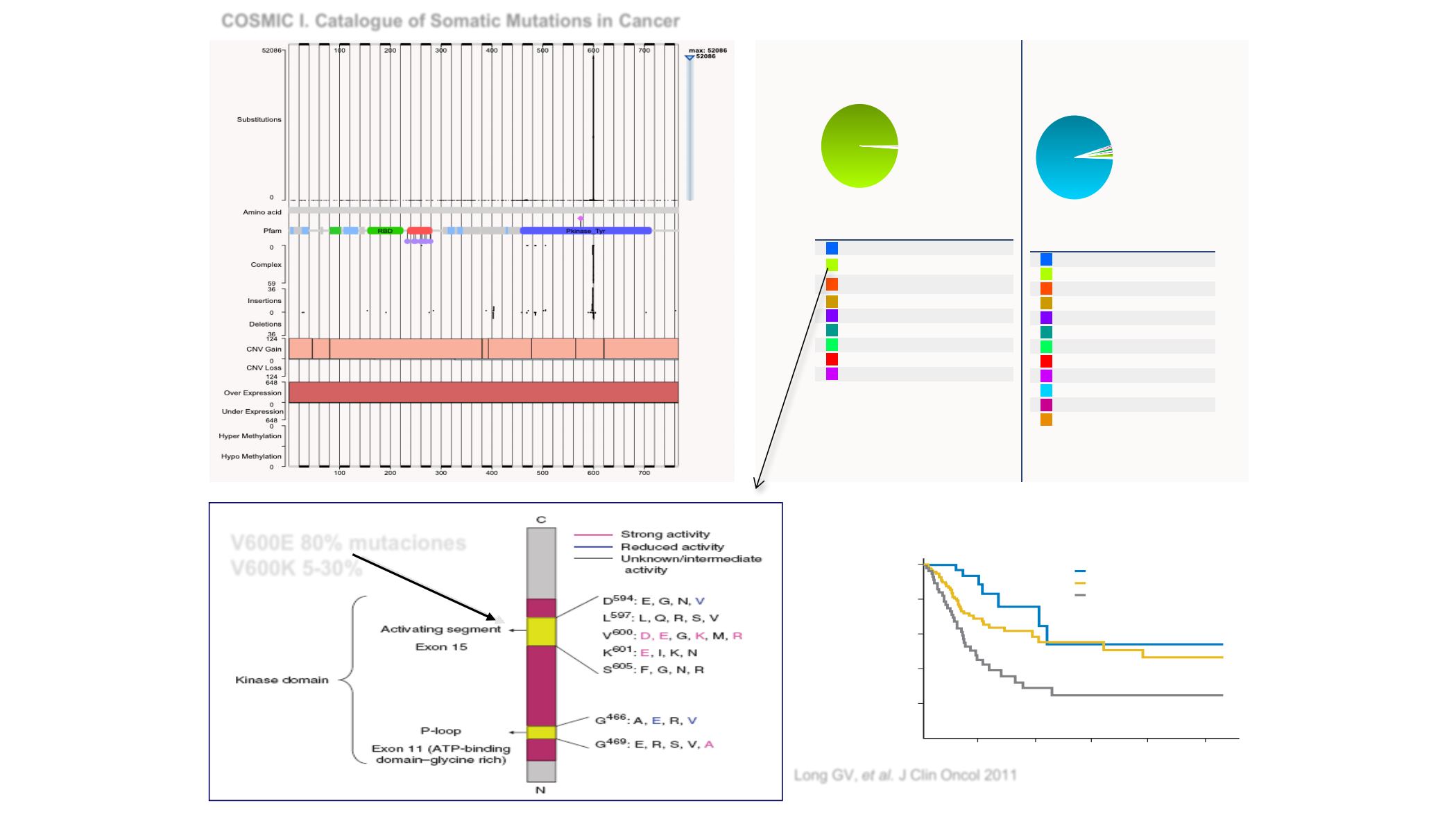
Colour Mutation type
Number of
samples (%)
Nonsense substitution
44 (0.08%)
Missense substitution
53189
(98.99%)
Synonymous
substitution
170 (0.32%)
Inframe insertion
54 (0.10%)
Frameshift insertion
12 (0.02%)
Inframe deletion
33 (0.06%)
Frameshift deletion
19 (0.04%)
Complex mutation
82 (0.15%)
Other
212 (0.39%)
Total unique samples
53731
Summary
An overview of the types of mutation observed.
Colour Mutation
type
Number of
samples (%)
A>C
43 (0.15%)
A>G
414 (1.40%)
A>T
47 (0.16%)
C>A
46 (0.16%)
C>T
172 (0.58%)
C>G
34 (0.12%)
G>A
315 (1.07%)
G>C
146 (0.49%)
G>T
157 (0.53%)
T>A
28173 (95.42%)
T>C
83 (0.28%)
T>G
72 (0.24%)
Total unique samples
29524
Substitutions
A breakdown of the observed substitution
mutations.
There are
23993
substitutions
where the
nucleotide change is unknown.
Deletions
This histogram shows the distribution of deletion
size across samples. You can see
all samples with
deletions
.
Insertions
This histogram shows the distribution of insertion
size. You can see
all samples with insertions
.
There are
14
insertions
that could not be
classified.
Nature 2002
V600E 80% mutaciones
V600K 5-30%
Correlates of mutan
noma were site (trunk), ea
and superficial spreading
the findings of studies in ea
novel findingwas the corre
mitoses in the antecedent
study of primary, as oppos
mitoses was associated wi
Nevertheless, these findin
melanoma is biologically h
other genetic alterations t
observed an association of
cutaneous primary melan
recent report that a history
is an independent good
diagnosis of distant metast
0
Overall
P
< .001
A
v
C
P
< .003
B
v
C
P
= .006
A
v
B
P
= .138
A
No. at risk
BRAF
mutant on
inhibitor
38
18
7
5
3
3
Overall Survival (%)
Time (years)
100
80
60
40
20
1
2
3
4
5
A:
BRAF
mutant on inhibitor
B:
BRAF
wild-type
C:
BRAF
mutant no inhibitor
Long et al
Long GV,
et al.
J Clin Oncol 2011
COSMIC I. Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer








