Kudo M
et al
.
Lancet
. 2018;pii:S0140-6736(18)30207–1.
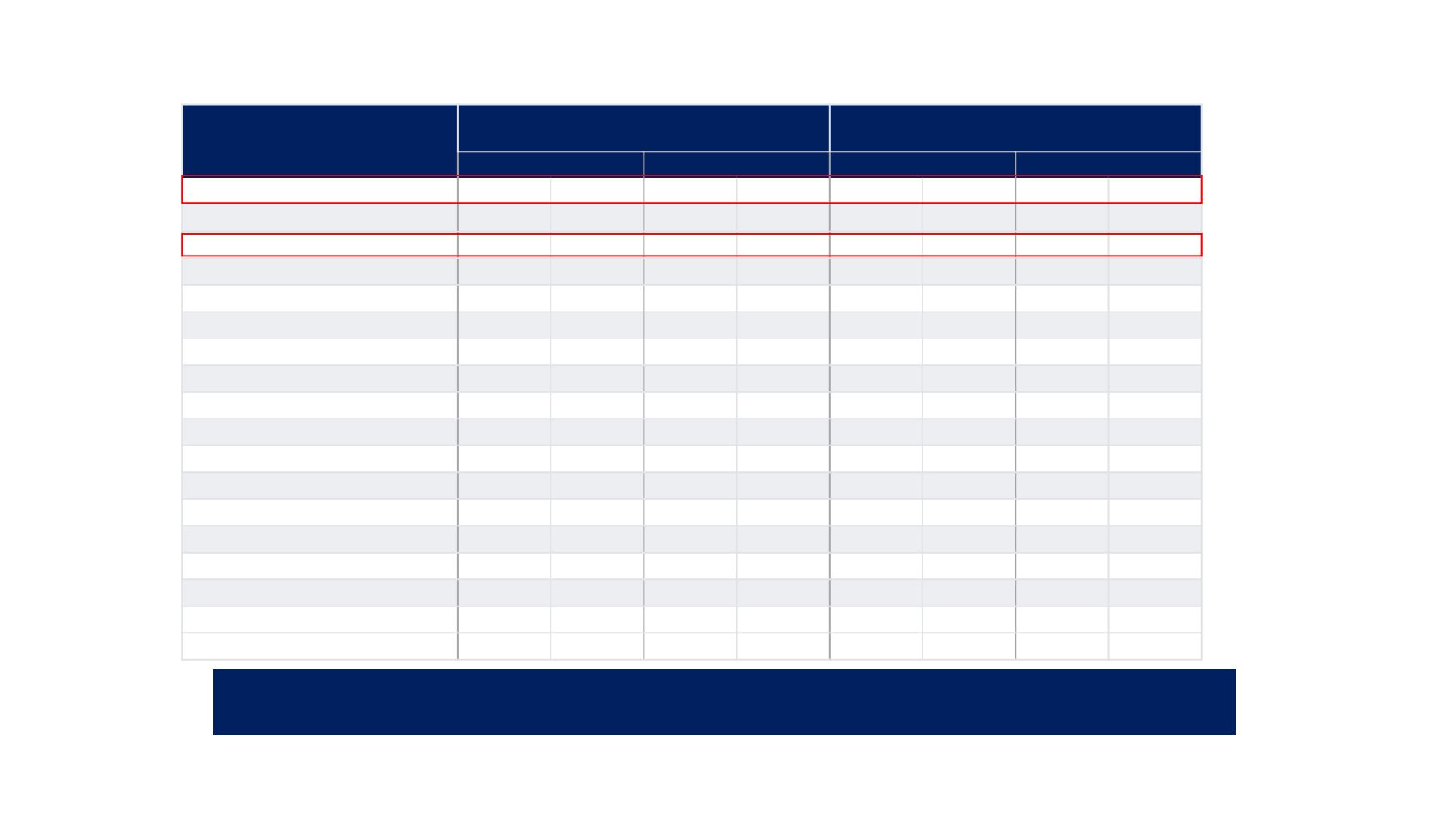
REFLECT TRIAL: Most Frequent TEAEs (≥15%)
AE, n, %
Lenvatinib
(N=476)
Sorafenib
(N=475)
Any grade
Grade 3/4
Any grade
Grade 3/4
PPE
128
27%
14
3%
249
52%
54
11%
Diarrhoea
184
39%
20
4%
220
46%
20
4%
Hypertension
201
42%
111
23%
144
30%
68
14%
Decreased appetite
162
34%
22
5%
127
27%
6
1%
Decreased weight
147
31%
36
8%
106
22%
14
3%
Fatigue
141
30%
18
4%
119
25%
17
4%
Alopecia
14
3%
0
0
119
25%
0
0
Proteinuria
117
25%
27
6%
54
11%
8
2%
Dysphonia
113
24%
1
<1%
57
12%
0
0%
Nausea
93
20%
4
1%
68
14%
4
1%
Abdominal pain
81
17%
8
2%
87
18%
13
3%
Decreased platelet count
87
18%
26
5%
58
12%
16
3%
Elevated AST
65
14%
24
5%
80
17%
38
8%
Hypothyroidism
78
16%
0
0%
8
2%
0
0%
Vomiting
77
16%
6
1%
36
8%
5
1%
Constipation
76
16%
3
1%
52
11%
0
0%
Rash
46
10%
0
0%
76
16%
2
<1%
Increased blood bilirubin
71
15%
31
7%
63
13%
23
5%
AE = adverse event; AST = aspartate aminotransferase; PPE = palmar-plantar erythrodysaesthesia; TEAE = treatment-emergent adverse event.
Fatal adverse events determined by the investigator to be related to lenvatinib treatment occurred in 11 (2%) patients and included hepatic failure (3),
cerebral haemorrhage (3) and respiratory failure (2). In the sorafenib group, treatment-related fatal adverse events occurred in four (1%) patients and
included tumour haemorrhage, ischaemic stroke, respiratory failure, and sudden death (one each).








