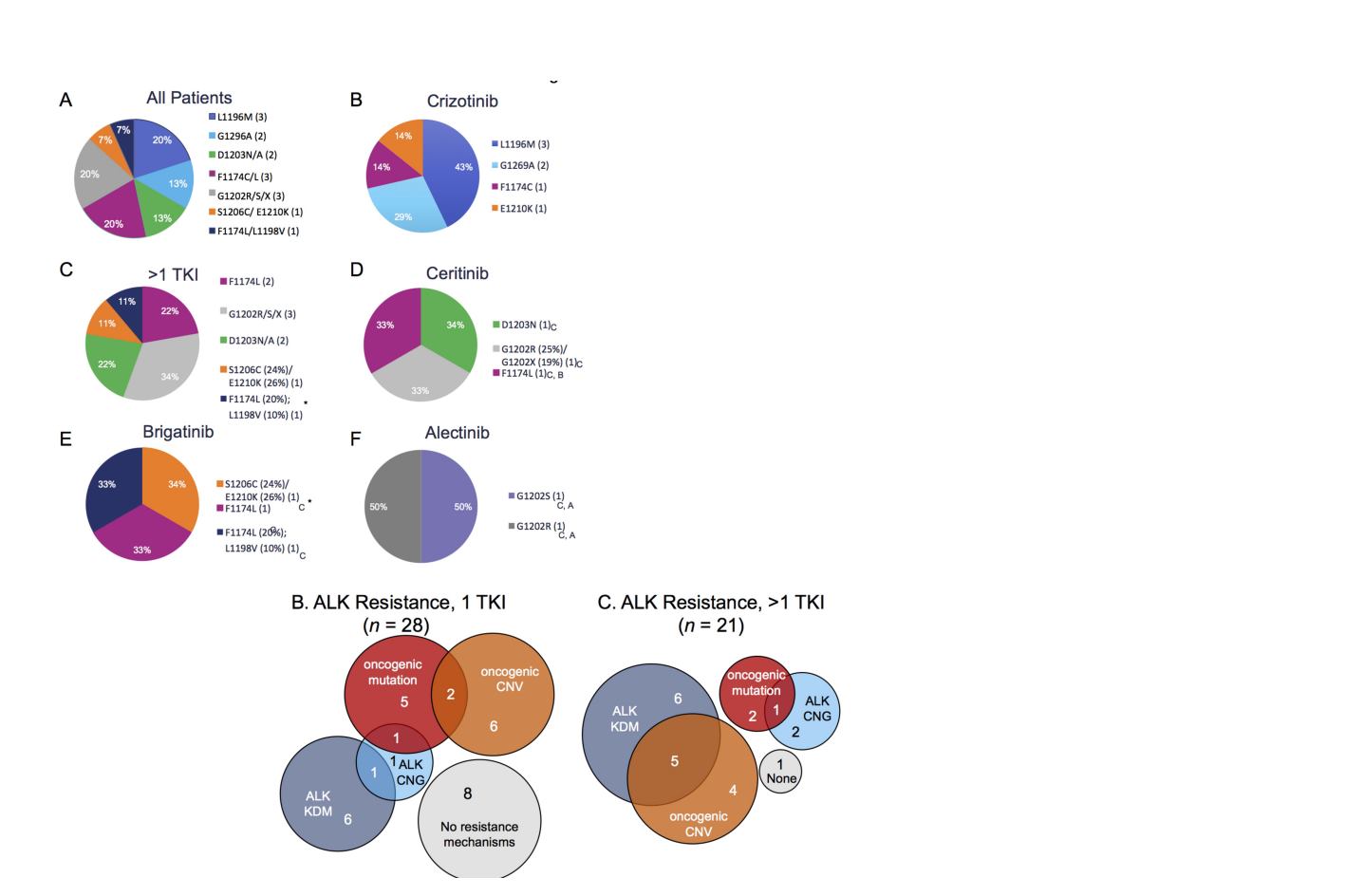
Resistance may be much more complex than kinase domain mutations
A putative TKI resistance mechanism was
identified in
86%
ALK+ patients:
•
Gene fusions (RET and NRG1) may be resistance
mechanisms to ALK inhibitors
•
Copy number variations (PDGFRA, KIT, KDR,
GNAS, NTRK1
…
) may explain some resistance to
ALK
•
Compound or multiple kinase domain mutations
(EGFR, KRAS, NOTCH, NF1, IDH1, RIT1
…
) appear
more common with NGS and /or ctDNA testing
Clin Cancer Res 2018;
DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2452








